Linear Programming is a powerful mathematical tool for optimizing outcomes, like maximizing profit or minimizing costs. Understanding its core concepts is crucial, and expert tutoring can bridge the gap from theory to practical mastery.

Imagine this: Sarah, a diligent college student, is staring at her calendar, completely overwhelmed. Mid-terms are just around the corner. She has a limited number of study hours before her exams in Calculus, Physics, and Economics. Each subject carries a different weight towards her final GPA, and she knows she needs a minimum score in each to pass. How can she allocate her precious time to maximize her overall score? It’s not just about studying hard; it’s about studying smart. Little does she know, Sarah’s dilemma is a classic optimization problem, the very kind that Linear Programming was designed to solve.
To better understand how this applies to real life, let’s visualize Sarah’s situation as an engineering system. The following illustration shows how inputs like time and energy are balanced to achieve the maximum output.
Linear Programming helps you balance limited resources (like time) to achieve the best possible outcome.
Just like Sarah optimizes her study schedule, engineers use this same logic to optimize complex industrial systems.
If you’ve ever felt like Sarah, trying to make the best decision with limited resources, then you’ve already grasped the essence of Linear Programming (LP). It might sound intimidating, but it’s a practical and powerful tool that shapes our world in countless ways, from the products on our store shelves to the flight paths of our airplanes. This article will demystify this fascinating subject, explore its real-world applications, and guide you on how to master it.
What Exactly is Linear Programming? The Core Concepts Explained
At its heart, Linear Programming is a mathematical method for finding the best possible outcome (like maximum profit or lowest cost) in a given situation. The key is that all the requirements and limitations of the situation must be expressible as linear relationships. Think of them as rules of the game, all written in straight-line equations. To get started, you need to understand three core components.
The Building Blocks: Objective Function, Constraints, and Decision Variables
Let’s go back to Sarah’s study problem to make this clear.
- Decision Variables: These are the things you have control over. For Sarah, the decision variables are the number of hours she chooses to study for Calculus (let’s call it x), Physics (y), and Economics (z).
- The Objective Function: This is the goal you want to achieve, expressed as a mathematical equation. If Sarah knows how much each hour of study for a subject is likely to improve her grade, her objective would be to maximize her total grade points. The equation might look something like: Maximize P = 5x + 4y + 3z, where the numbers represent the “point value” of each study hour.
- The Constraints: These are the limitations or rules you must follow. Sarah can’t study for an infinite amount of time. Her constraints might include:
- Total Study Time: x + y + z ≤ 40 hours.
- Minimum Subject Time: x ≥ 5, y ≥ 8, z ≥ 3 to ensure she covers the basics.
- Non-Negativity: x, y, z ≥ 0 (she can’t study for a negative number of hours!).
Once you define these three elements, you have officially framed a Linear Programming problem. The challenge, and where many students seek Linear Programming homework help, is translating a complex word problem into this neat structure.
Mathematical notation can sometimes look intimidating, so let’s break down the formula into its three essential building blocks. The diagram below maps the math directly to its purpose.
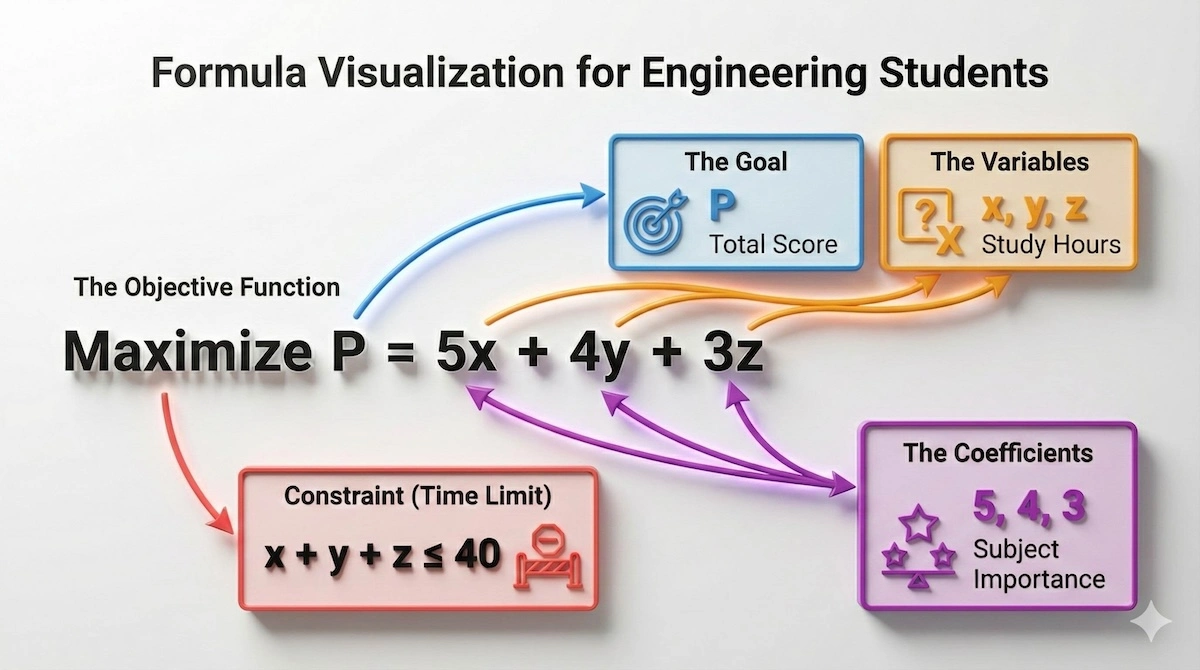
Every LP problem has three parts: the variables you control, the goal you want to reach, and the rules you must follow.
Once you can identify these three components—the goal, the variables, and the rules—you can set up any linear programming problem.
The Feasible Region: Visualizing Your Options
When you have only two decision variables (like studying for just Calculus and Physics), you can plot the constraints on a graph. Each constraint inequality defines a region, and the area where all these regions overlap is called the “feasible region.” This shaded area represents all the possible solutions that don’t break any of your rules. A fundamental theorem of Linear Programming states that the optimal solution—the absolute best outcome—will always be found at one of the corner points (vertices) of this feasible region. You just need to test the objective function at each corner to find the winner.
It is easy to get lost in the algebra, so use this roadmap to keep your problem-solving on track. This flowchart outlines the standard Graphical Method process step-by-step.
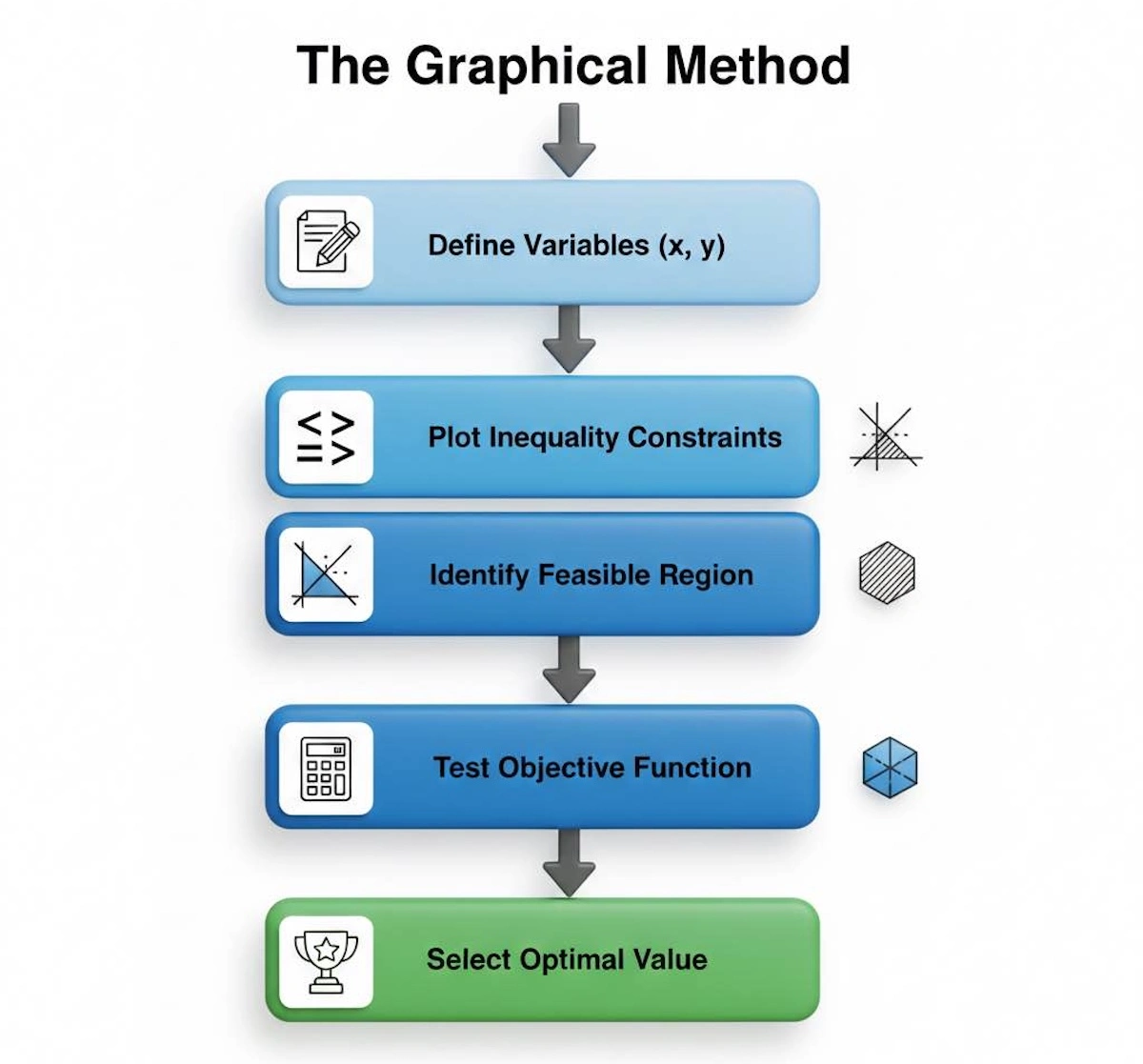
Follow these steps to solve any 2-variable linear programming problem using the graphical method.
Following this systematic sequence ensures you don’t miss the critical step of testing the corner points.
Why Does Linear Programming Feel So Challenging?
If it’s just about finding corners on a graph, why do so many students find themselves searching for a Linear Programming tutor? The difficulty often creeps in when the problems become more complex.
First, the transition from abstract theory to practical application is a huge leap. Formulating the problem correctly is often harder than solving it. A single misplaced number or incorrect inequality can send you down a completely wrong path.
Second, the graphical method only works for two variables. What about Sarah’s three subjects? Or a real-world problem with hundreds of variables? For that, you need more advanced techniques like the Simplex method, which involves a series of algebraic steps. While powerful, the Simplex algorithm can be tedious and confusing. It’s easy to get lost in the tables and calculations. A skilled Linear Programming teacher can be invaluable in making these complex methods intuitive.
Real-World Magic: Where Linear Programming Makes a Difference
LP isn’t just an academic exercise; it’s the invisible engine behind modern efficiency. The global market for prescriptive analytics, which heavily relies on LP and other optimization techniques, was valued at over USD 10 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, according to Grand View Research. This growth is fueled by companies striving for peak efficiency.
Business and Economics: Maximizing Profit, Minimizing Cost
Imagine a company that produces three different products. Each product requires a certain amount of time on different machines and uses different amounts of raw materials. The company has a limited number of machine hours and a fixed supply of materials. Using LP, the company can determine the exact number of each product to manufacture to maximize its profit without exceeding its resources. This is a classic problem where expert Linear Programming tutoring can help a student grasp the business application.
Logistics and Transportation: The Ultimate Routing Puzzle
Linear Programming isn’t just for textbooks; it powers the engines of the global economy. Here is a quick snapshot of how four major industries rely on these calculations every day.
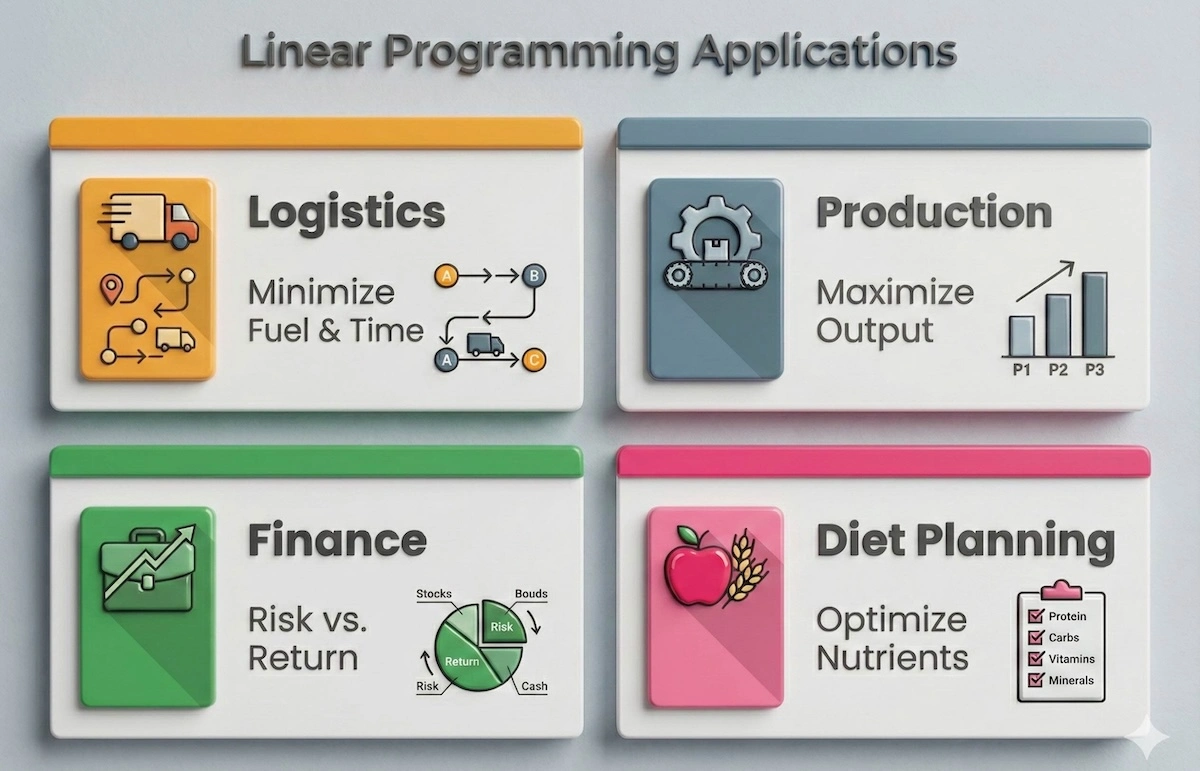
From delivering packages to managing portfolios, Linear Programming powers efficiency across these major industries.
As you can see, whether it is minimizing fuel for UPS or optimizing a financial portfolio, the underlying math is exactly the same.
How does a company like UPS or Amazon deliver millions of packages so efficiently every day? The answer lies in a field called Operations Research, where Linear Programming is a cornerstone. They use it to solve massive routing problems: finding the shortest paths for their trucks to take, minimizing fuel consumption and delivery times. UPS famously invested in a system called ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation), which uses sophisticated algorithms to optimize routes, saving the company an estimated 100 million miles and 10 million gallons of fuel each year. When students get Linear Programming assignment help, they are often tackling smaller versions of these exact problems.
Engineering and Beyond: From Diet Planning to Network Flows
The applications are virtually endless. Nutritionists use LP to create optimal, low-cost diet plans that meet specific nutritional requirements. Engineers use it to manage water resources or design resilient networks. Even financial analysts use it to create investment portfolios that maximize returns for a given level of risk. Mastering this subject opens doors to a wide array of high-demand career fields.
Navigating Your Studies: When to Seek Linear Programming Homework Help
It’s late at night. You’re staring at a problem about a factory’s production schedule, and the words are starting to blur. You’ve drawn the graphs, set up the equations, but the answer just isn’t coming out right. This is the moment when frustration sets in. Seeking help isn’t about giving up; it’s about getting a fresh perspective to unlock your understanding.
Consider looking for Linear Programming hw help if you are:
- Struggling to translate complex word problems into mathematical models.
- Getting lost in the iterative steps of the Simplex method or other algorithms.
- Unsure how to interpret the results of your solution (what does the “shadow price” even mean?).
- Feeling like you understand the lectures but can’t solve the problems independently.
Are you struggling to determine if you need extra support? Follow this simple decision path to diagnose your current standing with the material.
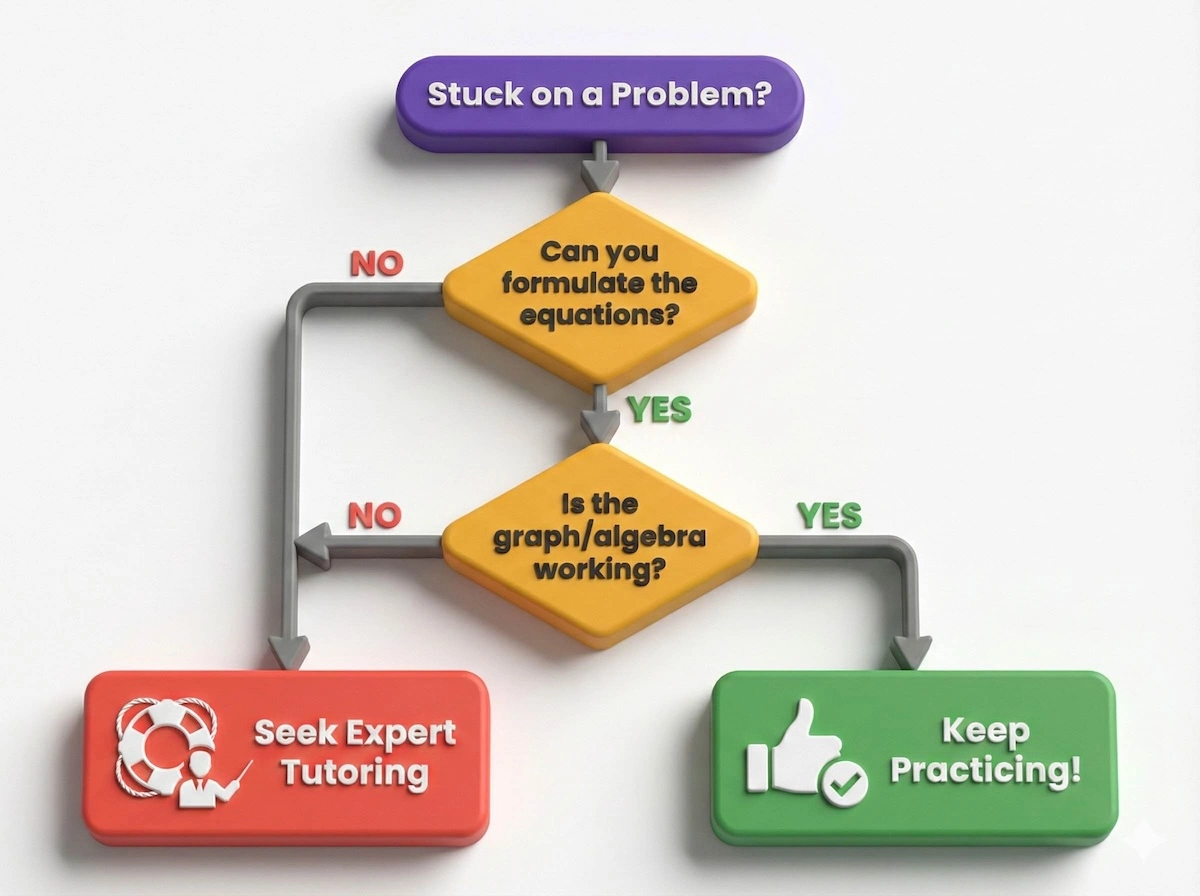
Not sure if you need a tutor? Follow this simple path to find out.
If you landed in the red zone, reaching out to an expert tutor now can save you hours of frustration later.
This is where personalized Linear Programming teaching can make all the difference. An expert can quickly identify where you’re going wrong and provide targeted explanations that resonate with your way of learning.
Finding the Right Guide: What to Look for in a Linear Programming Tutor
Once you’ve decided to get help, the next step is finding the right person. The goal isn’t just to get answers but to build genuine understanding. When you decide to hire a Linear Programming tutor, look for a few key qualities.
Expertise and Experience
Your tutor should have a strong, verifiable background in mathematics, operations research, engineering, or a related field. They should not only know the material but also have experience explaining it to others. Look for someone who can provide clear, step-by-step explanations for complex topics.
Tailored Teaching Style
A great tutor doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all approach. They take the time to understand your specific weak points and adapt their teaching method to you. Effective Linear Programming tutoring focuses on your “aha!” moments, building your confidence along with your skills.
The Convenience of Online Learning
In today’s connected world, you’re no longer limited to local tutors. Finding a Linear Programming tutor online gives you access to a global pool of talent. Platforms that offer Linear Programming tutoring online provide incredible flexibility, allowing you to schedule sessions that fit your busy life. Plus, with tools like interactive digital whiteboards, screen sharing, and session recordings, the learning experience can be even more effective than in-person instruction.
Your Path to Success in Linear Programming
Linear Programming is more than just a chapter in your textbook. It’s a way of thinking—a structured approach to making optimal decisions in a world full of constraints. It’s a skill that is highly valued in business, technology, and science.
Embracing its challenges is the first step. Whether you work through the problems on your own or with the expert guidance of a tutor, the effort you put in will pay dividends. Like Sarah, you can learn to look at a complex problem, break it down into its essential parts, and find the very best path forward. And that’s a skill that will serve you well long after the final exam is over.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1 What is the main goal of Linear Programming?
The main goal is to find the best possible outcome, such as maximum profit or minimum cost, given a set of linear constraints.
Q2 Is Linear Programming only used in math class?
No, it is widely used in business, engineering, logistics, and economics to solve real-world optimization problems.
Q3 What is the hardest part of Linear Programming?
For many students, the most challenging part is correctly translating a real-world word problem into a mathematical model.
Q4 Can a tutor really help with my LP homework?
Yes, a great tutor can provide personalized guidance to help you understand difficult concepts and solve challenging problems.
Q5 Is online tutoring effective for a subject like this?
Absolutely, online tutoring offers flexible scheduling and interactive tools that make learning complex topics like LP very effective.
Q6 How much does Linear Programming tutoring cost?
Costs can vary, but quality tutoring is often available at reasonable rates, typically ranging from $20 to $40 per hour.
Related Subjects
Constraints
Convex Optimization
Discrete Optimization
Genetic Algorithms
Simplex Method
******************************
This article provides general educational guidance only. It is NOT official exam policy, professional academic advice, or guaranteed results. Always verify information with your school, official exam boards (College Board, Cambridge, IB), or qualified professionals before making decisions. Read Full Policies & Disclaimer , Contact Us To Report An Error
